Unveiling the Secrets of Cinema Revenue Success
Introduction
As a seasoned professional with over two decades of experience in accounting and robust expertise in data science, I bring a unique analytical perspective to financial analysis. This project on cinema sales data draws from my extensive background in financial management and revenue recognition, applying advanced analytics to uncover key drivers of cinema sales and optimize business strategies.
Project Objectives
This project aims to leverage deep insights from accounting and data science to understand and amplify the factors influencing cinema sales, thereby boosting revenue potential.
Dataset Overview
The dataset encompasses detailed records of ticket sales, seating capacities, show timings, and other pertinent data, amounting to over 142,000 transaction records across various cinema and film codes. This rich dataset provides the foundation for a comprehensive analysis aimed at uncovering underlying sales drivers.
Technologies and Tools Used
Enhanced by my recent certification as a Certified Data Science Professional in Python from DataCamp, my advanced Python skills were pivotal in this project. Utilizing libraries like NumPy, pandas, matplotlib, scikit-learn, and Seaborn, I conducted sophisticated data manipulations, statistical modeling, and insightful visualizations.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Through extensive exploratory analysis, I identified crucial patterns and variables, ensuring the accuracy of data type conversions and analyses, which are fundamental to the success of this project.
The line graph below illustrates the patterns in our daily total sales data, revealing how different times of the year, movie releases, and other factors influence cinema revenue.
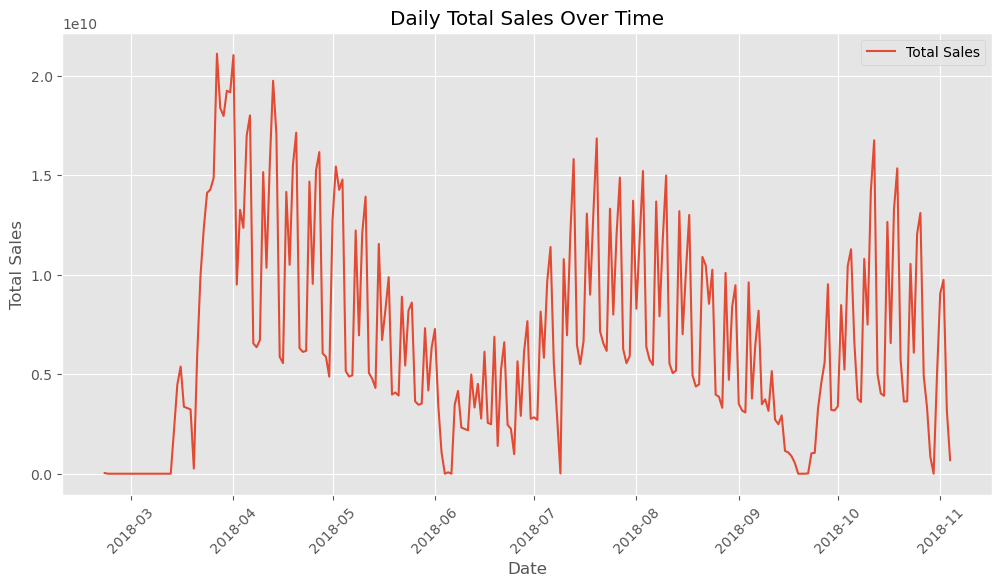 Figure 2: The line graph traces daily total sales, offering insight into the sales trends over time and helping to identify periods of high and low demand.
Figure 2: The line graph traces daily total sales, offering insight into the sales trends over time and helping to identify periods of high and low demand.
Data Preprocessing
Significant adjustments made to ensure data quality included:
- Filling Missing Values: Addressing gaps in the ‘capacity’ data by applying average values. My background in financial forecasting and analysis was crucial in determining the most statistically appropriate method for handling missing data.
- Adjusting Show Times: Standardizing show times to a 24-hour format, leveraging my expertise in ensuring data accuracy and compliance with financial standards.
- Handling Overcapacity: Correcting any instances where occupancy percentages exceeded plausible limits, a task aligned with financial auditing practices where accuracy and regulatory compliance are paramount.
# Calculate the mean capacity for each cinema_code, excluding negative values
mean_capacity_per_cinema = df[df['capacity'] > 0].groupby('cinema_code')['capacity'].mean()
# Fill negative capacity values with the mean capacity of the corresponding cinema_code
df.loc[df['capacity'] < 0, 'capacity'] = df.loc[df['capacity'] < 0, 'cinema_code'].apply(
lambda x: mean_capacity_per_cinema.get(x, np.nan)
)
# Handle cases where mean capacity is not available
df['capacity'].fillna(df['capacity'].mean(), inplace=True)
- Encoding Categorical Variables: Converting categorical data into numeric formats, a skill honed through my experience with financial databases and ensuring compliance with data standards.
Model Selection
I employed robust machine learning models such as Random Forest and Gradient Boosting to manage outliers and skewed distributions effectively. Parameter optimization was achieved through randomized search techniques, reflecting a methodical approach in predictive accuracy.
Actionable Strategies and Key Insights
When evaluating the impact of different cinema features on sales performance, it’s crucial to identify which variables play pivotal roles. The chart below aggregates feature importances from both Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting (GB) models, shedding light on the predictors that are most influential in forecasting sales.
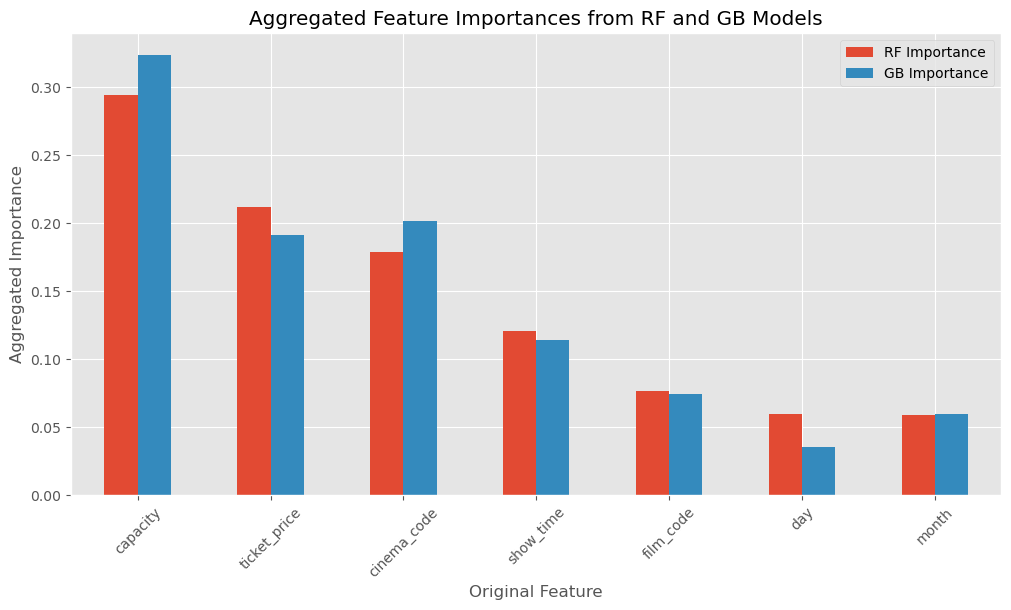 Figure 2: Bar chart displaying aggregated feature importances from RF and GB models, highlighting the predictive power of features such as capacity, ticket price, and cinema code.
Figure 2: Bar chart displaying aggregated feature importances from RF and GB models, highlighting the predictive power of features such as capacity, ticket price, and cinema code.
- Pricing Optimization: Recommended dynamic pricing models to maximize earnings based on time and film type.
- Capacity Utilization: Provided strategic scheduling recommendations to enhance seat utilization.
- Targeted Marketing: Developed marketing strategies focused on the most influential factors affecting customer attendance and preferences.
- Show-Time Optimization: Proposed adjustments to show times based on patterns that maximize attendance and revenue.
Challenges and Learning Experiences
Handling complex data structures and ensuring the integrity of predictive models required sophisticated data manipulation strategies:
- Binary Encoding: Implementing binary encoding to manage high cardinality features and later reverting encoded features to their original formats to preserve interpretability.
# Use category encoders to encode categorical variables; otherwise too many features to handle (over 300)
import category_encoders as ce
# List of categorical columns to be binary encoded
categorical_columns = ['film_code', 'cinema_code', 'month', 'day']
# Create a binary encoder
binary_encoder = ce.BinaryEncoder(cols=categorical_columns)
# Fit and transform to produce binary encoded dataFrame
df_encoded = binary_encoder.fit_transform(df)
Reflections and Looking Ahead
Merging financial management with data science in this project highlighted the powerful synergy between accounting precision and analytical modeling. It underscored the value of integrating comprehensive financial understanding with data science capabilities in addressing real-world business scenarios.
Discover the Full Story
Dive into the comprehensive analysis here.
Explore the Technical Journey
For a detailed breakdown, including code and visuals, view the project notebook on NBViewer.
